Have you ever run the ls command on the root of a Linux system and wonder what all the directories are and what they contain?
The root directory layout of a Linux system can initially seem a little confusing, with directories like /usr being name user but not really being used as a location for users files.
For this blog post I am going to be using a Raspberry Pi 4 and Raspbian (Linux) to take a brief look at the Linux root directory.
Directory Layout

When the ls command is run at the root it returns the following directories:
- bin
- dev
- home
- lost+found
- mnt
- proc
- run
- srv
- tmp
- var
- boot
- etc
- lib
- media
- opt
- root
- sbin
- sys
- usr
The Directories
/bin

bin is short for binary, and the /bin directory is where executables (e.g. programs) in binary format are stored. When you run ls, cp, grep, chmod etc they are all binaries stored in this directory.
/dev

Contains various device files that the Linux system relies on, including devices Linux installed during the operating system installation.
/home
Contains the user’s home folder, which then contains the user’s deskop, documents etc.
/lost+found
If the fsck command finds any data corruption on a partition it places the corrupted data into the lost+found directory.
/mnt
Can be used to mount additional drives into the current file hierarchy.
/proc
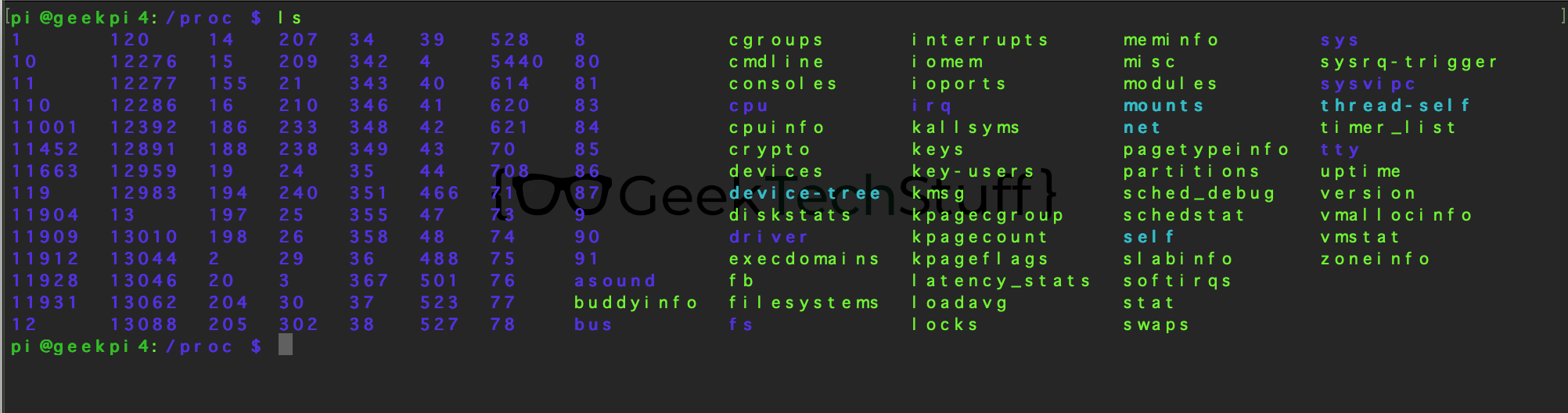
Contains information on currently running processes and system resource usage.
/run

Run time data since the systems last boot.
/srv
Server information being served/offered by the computer.
/tmp
Contains temporary files.
/var

Contains cache files and the log directory.
/boot

Contains the Linux boot loader files.
/etc
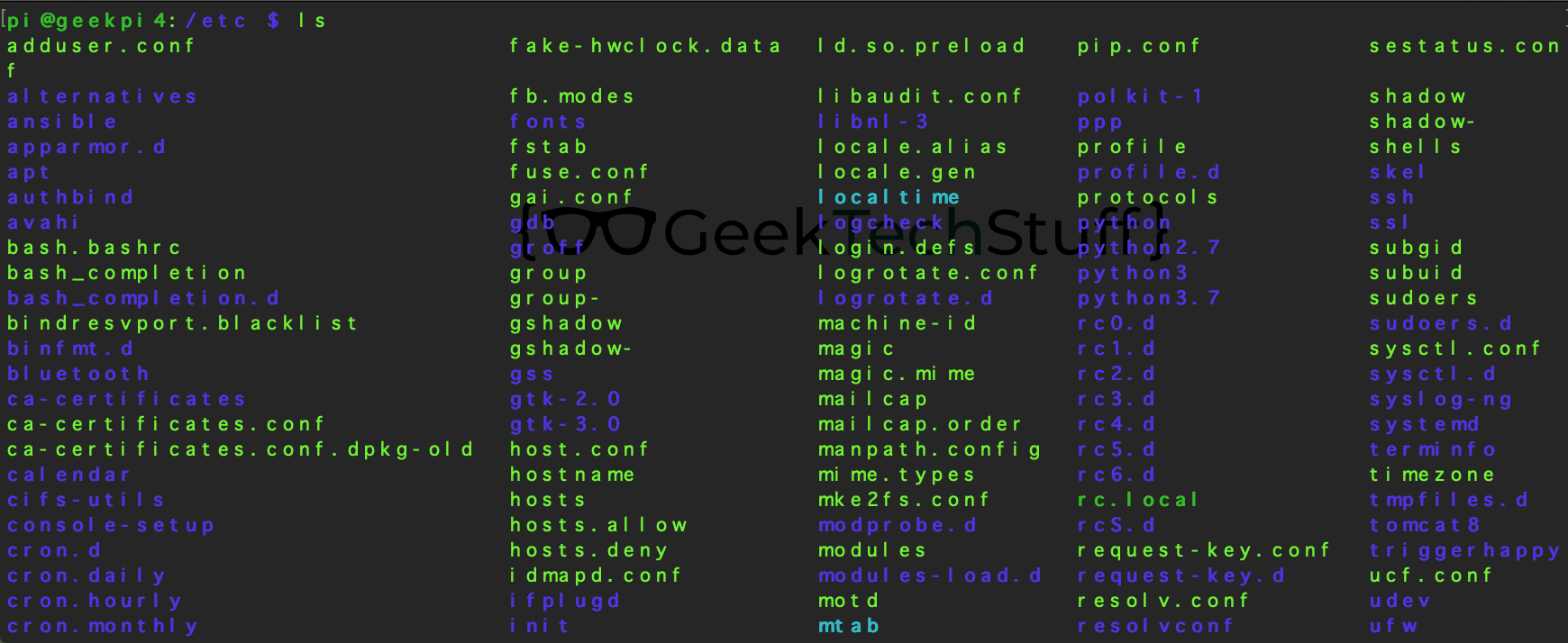
Configuration files used by the system or software on the system.
/lib
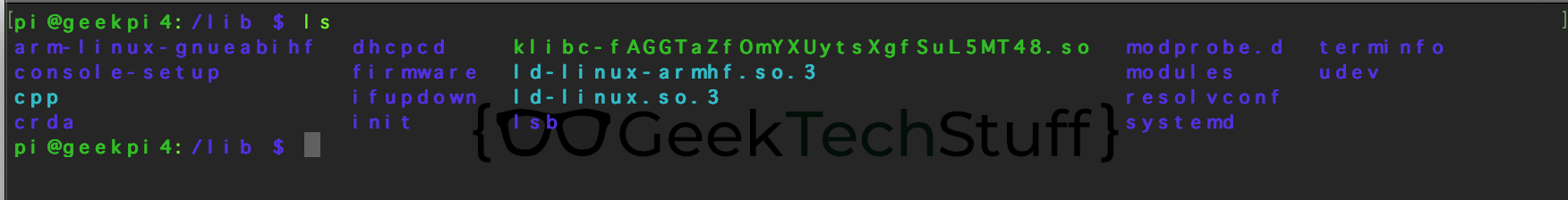
Libraries that are called by files in /bin and /sbin.
/media
Location where removable media (e.g. USB pen drives) connect to.
/opt
I think this was for “optional” software, i.e. 3rd party software.
/root
The root user’s home directory.
/sbin

System binaries, i.e. the system (s) version of /bin.
/sys
System files containing information about the system, devices and the kernel.
/usr
Does not contain user files. Large parts of the Linux operating system are contained in the /usr section.
Want To Find Out More?
The best way to learn about Linux is to explore it and that can be done by installing Linux in a virtual machine, booting from a Linux USB drive / Live disc, or installing Linux as your operating system (OS).
Wikipedia on Filesystem Hierarchy.


You must be logged in to post a comment.